Local development
Setup - Up and running in less than 5 minutes
Depending on your preference, you can either use Docker Sail or Laravel Herd to set up a local development environment for SaaSykit.
-
Fork/Clone the SaaSykit repository
There are two ways you can use the SaaSykit repository; clone it locally and push it to your own repository, or fork the repository to your GitHub account.
Clone the repository & push to your own repository (recommended way)
Github has a limitation that allows you to only fork a repository once. This means that if you're planning to use SaaSykit to build multiple projects, or if you want to both use "SaaSykit" and "SaaSykit Tenancy" (which is a fork of SaaSykit) at the same time, you're better off cloning the SaaSykit repository and pushing it to your own repository.
-
Clone the SaaSykit repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/saasykit/saasykit.gitFor SaaSykit Tenancy, you can clone the repository using the below command:
git clone https://github.com/saasykit/saasykit-tenancy.git-
Change into the project directory:
cd saasykitFor SaaSykit Tenancy, you can change into the project directory using the below command:
cd saasykit-tenancy
-
-
Rename the default "remote" to "upstream" (the source you’re tracking):
git remote rename origin upstream- Create a New Repository on you GitHub account for your new project
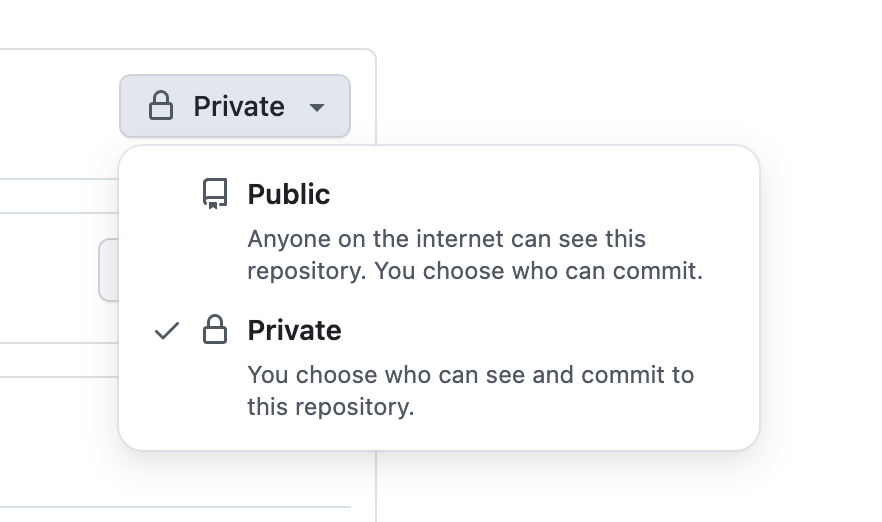
ImportantPlease make sure that your new repository is "private". If you make it public, you will be exposing the entire SaaSykit source code including all the premium features that are only available to paid users.
-
Add a new "remote" called "origin" to (your own repository):
git remote add origin https://github.com/your-username/your-repo.git -
Push the code to your repository:
git push -u origin main
Fork the repository
If you decide to go this way, fork the SaaSykit repository to your GitHub account. You can do this by clicking the "Fork" button in the top right corner of the SaaSykit repository or SaaSykit Tenancy repository.
Once you have forked the repository, you can clone it to your local machine using the below command:
git clone [your-forked-repository-url] -
-
Set up the local development environment
- Laravel Herd
- Docker Sail
Laravel Herd is One click PHP development environment that lives in the menu bar and makes it easy to create and manage local development environments. It currently only works with macOS & Windows.
- Download and install Laravel Herd. Check the following video for more information on how to install & configure it:
- Once you have Laravel Herd installed, clone your SaaSykit forked repository that you created above into your Herd projects directory. Depending on your operating system, the Herd directory can be found in the following locations:
- macOS
- Windows
~/Herd check the Herd documentation for more information.
%USERPROFILE%/Herd check the Herd documentation for more information.
- Open the terminal and navigate to the SaaSykit directory in the Herd projects directory:
- macOS
- Windows
cd ~/Herd/saasykit
cd %USERPROFILE%/Herd/saasykit
-
SaaSykit needs a database run, so you will need to install a database server locally (or if you have a Pro Herd license, then you will be able to use the database server provided by Herd). You can use MySQL or PostgreSQL for this.
-
Install composer dependencies
composer install --ignore-platform-reqs --no-interaction --no-scripts --prefer-dist -
Copy .env.example to .env
cp .env.example .env -
Open the
.envfile and make sure that the ports defined under# local development settingsare not in use by any other application on your machine. If they are, you can change them to any other port of your choice. Also make sure to update the database settings to match your local database settings. Another important thing to note is that you will need to update theAPP_URLto match the URL that Herd provides you with. This is usually{directory-name}.testfor example:http://saasykit.test. -
Generate app secret
php artisan key:generate -
Run migrations
php artisan migrate -
Run seeders
php artisan db:seed -
Link storage
php artisan storage:link -
If you don't have Node & NPM installed, install them, then install npm dependencies
npm install -
Build assets
npm run build -
Run the NPM (vite) watcher
npm run dev
Now navigate to the [name-of-your-project-folder].test (for example saasykit.test) in your browser. You should see the SaaSykit home page! 🎉
Sail is a light-weight command-line interface for interacting with Laravel's default Docker development environment. Sail provides a great starting point for building a Laravel application using PHP, MySQL, and Redis without requiring prior Docker experience. You will need to have Docker installed on your machine to use Sail.
If you prefer to watch a video tutorial, you can watch the below video to get started: (all the commands used in the video are also listed below):
Once you get docker installed on your machine, you can follow the below steps to get started with SaaSykit.
-
Change into the project directory (if you haven't already)
cd [your-forked-repository-name] -
Install composer dependencies
composer install --ignore-platform-reqs --no-interaction --no-scripts --prefer-dist -
Copy .env.example to .env
cp .env.example .env -
Open the
.envfile and make sure that the ports defined under# local development settingsare not in use by any other application on your machine. If they are, you can change them to any other port of your choice. -
Run the below command to start the docker containers
./vendor/bin/sail up -d -
Generate app secret
./vendor/bin/sail artisan key:generate -
Run migrations
./vendor/bin/sail artisan migrate -
Run seeders
./vendor/bin/sail artisan db:seed -
Link storage
./vendor/bin/sail artisan storage:link -
Install npm dependencies
./vendor/bin/sail npm install -
Build assets
./vendor/bin/sail npm run build -
Run the NPM (vite) watcher
./vendor/bin/sail npm run dev
That's it! 🎉 Open the browser and go to http://localhost:8080 (or change the port here if you choose another port in .env.). You should see the SaaSykit home page.
Creating an Admin User
You can create an admin user by running the below command:
- Laravel Herd
- Docker Sail
php artisan app:create-admin-user
./vendor/bin/sail artisan app:create-admin-user
You can also pass in the --email and --password options to the command to set the email and password for the admin user. If you don't pass in these options, the command will prompt you to enter email and will automatically generate a random password for you.
- Laravel Herd
- Docker Sail
php artisan app:create-admin-user [email protected] --password=password123
./vendor/bin/sail artisan app:create-admin-user [email protected] --password=password123
With that use you can access the admin panel by going to /admin and logging in with the credentials you just created.
Demo data
SaaSykit comes with demo data that you can use to test the application and see how things look and work. The demo data includes products, plans, discounts, blog posts, and users, etc.
To install the demo data, you can run the below command:
- Laravel Herd
- Docker Sail
php artisan db:seed "Database\Seeders\Demo\DemoDatabaseSeeder"
./vendor/bin/sail artisan db:seed "Database\Seeders\Demo\DemoDatabaseSeeder"
How to Build a SaaS with SaaSykit
Ready to get started? Watch the below video to learn how to build a SaaS application using SaaSykit:
Development Resources
SaaSykit is based on the awesome Laravel framework. If you are new to Laravel, you can check out the Laravel documentation to get started with Laravel.
If you are already familiar with Laravel, you will easily be able to get started with SaaSykit as it follows the same coding standards and best practices as Laravel.
The admin panel and user dashboard are built using Filament. Filament is a beautiful, modern, and responsive admin panel for Laravel applications.
Keeping your fork up to date
To keep your fork up to date with the original repository, you can follow the below steps:
-
Add the original repository as a remote
For SaaSykit use:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/saasykit/saasykit.gitFor SaaSykit Tenancy use:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/saasykit/saasykit-tenancy.git -
Fetch the branches and commits from the original repository
git fetch upstream -
Merge the changes from the original repository into your local branch
git merge upstream/main
Then you can push the changes to your forked repository.
It's a good practice to regularly keep your fork up to date with the original repository to get the latest features and bug fixes. This will also help you to avoid/reduce the merge conflicts in case you edited the same files that was updated in the original repository.
Running automated tests
SaaSykit comes with an ever-growing set of automated tests that cover the critical components of the application.
While some developers prefer to always run tests against a sqlite database, this might leave some bugs undetected that will be only visible when running against a real database like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
So it's important to configure your automated tests to use the same database type you plan to use in production.
You'll need to edit your .env.testing file to match your local database settings.
For example, if you are using MySQL, you can update the .env.testing file to look like this:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=saasykit_test
DB_USERNAME=YOUR_USERNAME
DB_PASSWORD=YOUR_PASSWORD
For PostgreSQL, you can update the .env.testing file to look like this:
DB_CONNECTION=pgsql
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=5432
DB_DATABASE=saasykit_test
DB_USERNAME=YOUR_USERNAME
DB_PASSWORD=YOUR_PASSWORD
Sometime for certain operating system you might need to switch "localhost" to "127.0.0.1" in the .env.testing file in case the host is not being resolved.
Then you can run the tests using the below command:
- Laravel Herd
- Docker Sail
php artisan test
./vendor/bin/sail test